4 Marijuana and Brain Development in Adolescents
Margaret Crisologo
Introduction
Opinions on marijuana have varied through the years. It went from a drug feared to cause violent acts and lead to insanity in the 1930s to being seen as a potential medication for cancer pain and seizures in the 2010s. As a result, a few states have legalized the medicinal and recreational use of marijuana. However, recreational marijuana may be harmful when misused, especially in adolescence (ages 10 to 19). As of 2018, six percent of 12th graders, three percent of 10th graders, and one percent of 8th graders reported daily cannabis use in the United States (Hammond et al., 2020). Cannabis produced today contains higher levels of THC (see Chapter 5 for more information). With the introduction of edibles as a source of marijuana, it is easier to ingest excessive amounts of THC without realizing it (Centers for Disease Control, 2021; Testai et al., 2022).
What is Marijuana?

Cannabis refers to products from the Cannabis sativa plant (National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, 2019). Marijuana refers to the dried leaves, flowers, stems, and seeds from the Cannabis Sativa plant that contains tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) (National Institute on Drug Abuse, 2019). Marijuana has both medicinal use and recreational use. Medicinal marijuana is cannabis taken orally or by nasal spray to relieve symptoms of a medical condition (Alcohol and Drug Foundation, 2022). Medical marijuana may help with seizures, pain, anxiety management, and help with reducing inflammation. Recreational marijuana is cannabis used for personal enjoyment (Leafly, n.d.). Unlike medical marijuana, recreational marijuana contains more THC, the chemical responsible for feeling high.
History of Cannabis
When first introduced to America in the 1600s, cannabis was primarily grown to make clothes, ropes, sails, paper, and oil (History.com, 2017). The unique medicinal and recreational properties helped increase the spread of cannabis worldwide. It was not until the late 19th century that marijuana became used in medicine (University of Georgia, n.d.). However, increased immigration from Mexico negatively impacted attitudes around cannabis (University of Georgia, n.d.). Marijuana had become a drug that those of a higher socioeconomic status feared for its addicting and violence-causing capabilities, both of which are myths (Siff, 2014). By 1931, 29 states had passed laws prohibiting marijuana. By 1937, the Marijuana Tax Act was passed (University of Georgia, n.d.).
In 1970, Congress classified marijuana as a Schedule 1 drug by the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act (Siff, 2014). As a Schedule 1 drug, Congress deemed marijuana to have no accepted medical use and a high potential for abuse (United States Drug Enforcement Administration, n.d.). However, a few states began legalizing the use of marijuana, with California being the first state to legalize medical marijuana in 1996. Currently, 21 states have legalized the medical and recreational use of marijuana (M.J. Biz Daily, n.d.). Other states have enacted decriminalization laws (NORML, n.d.).
Effect of Legalization
Since the legalization of cannabis, few adolescents have perceived it as harmful. It has become more socially acceptable and seen as beneficial to health (Mennis et al., 2023; Geoffrion, n.d.). In 2018, about 1.6 million adolescents aged 12 to 17 used cannabis (Hammond et al., 2020). In 2022, roughly 30.7% of high school seniors reported using cannabis (National Institute on Drug Abuse, 2020b). Many adolescents are exposed to ads promoting edibles, vapes, and other cannabis products. In 2019, roughly one in three youth in states with legal recreational use interacted with marijuana brands on social media (University of Wisconsin-Madison, 2019). According to the University of Wisconsin-Madison, engaging with marijuana marketing is linked to adolescents’ being five to eight times more likely to use marijuana.
Effects of Marijuana on Adolescents
Effect on Brain Structure
The brain continuously develops from the moment of birth up until age 25. In adolescence, certain areas of the brain that affect impulse control, social behavior, and planning start to develop. During this time, the brain also undergoes maintenance, removing unused connections and improving those used to increase cognitive functioning (Dhein, 2020). Marijuana interacts with specific receptors within the brain, increasing or decreasing dopamine and glutamate levels in the brain. These receptors are involved in various activities, from appetite and memory to pain and inflammation (Genetic Science Learning Center, n.d.; Zou & Kumar, 2018; Testai et al., 2022; Ye, Cao, Wan, & Zhou, 2019).
However, some research has shown that heavy cannabis use can damage adolescent development (Dhein,2020; De Felice et al., 2023). Early cannabis use may thin or reduce the number of neurons that develop in specific brain areas, impairing the connection between locations (Dhein, 2020; Schmidt, 2021; Blest-Hopley et al., 2020). Areas of the brain affected by marijuana use include the hippocampus and the prefrontal cortex.
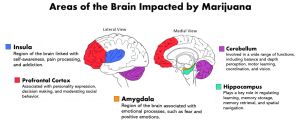
Effect on Brain Function
These structural changes and disruptions in normal brain development in youth could contribute to more significant and long-lasting changes in behavior and memory (Schmidt, 2021). Heavy cannabis use during adolescence may impair planning, abstract thinking, and impulse control (Weir, 2015). Other effects associated with marijuana use include poor memory, lack of motivation, trouble managing emotions, and poor sleep quality (Volkow et al., 2016; Jacobus et al., 2010). Additionally, daily use of marijuana during adolescence can increase the risk of addiction and the development of a cannabis use disorder (Geoffrion, n.d.). In 2017, 2% of adolescents aged 12 to 17 met the definition of cannabis use disorder (Hammond et al., 2020). Chapter 5, “Marijuana Overconsumption and Tolerance” discusses cannabis use disorder further. Overall, marijuana use can lead to difficulties in learning and lower intelligence (National Institute on Drug Abuse, 2021).
Social Impact of Marijuana Use
The effects of cannabis on the brain can negatively impact their future social standing and well-being. As a result of the impairments in learning, adolescents who used marijuana tended to have lower academic outcomes, leading to poor economic outcomes by their early 30s (Eckart, 2019). Poor educational development impacts racial and ethnic minorities more within the United States than those who are not. Racial and ethnic minorities may lack access to resources promoting academic achievement (Cyrus et al., 2021). Marijuana is also associated with a risk of developing or worsening mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression (Ali et al., 2019). Cannabis use may also increase risky behaviors and lead to a dependency on cannabis, negatively impacting future relationships (Ali et al., 2019; Ekcart, 2019).
Conclusion
Daily use of cannabis may reduce the number of neurons in some brain regions, impacting the brain’s ability to connect and send messages to each area. Cannabis can impair adolescents’ learning capabilities and increase the risk of developing a cannabis use disorder. Multiple interventions out there address cannabis use and substance use in general in the adolescent population, including Teen Marijuana Check-Up, which showed greater decreases in cannabis use compared to adolescents who did not use it. It has even been shown that a brief, three-session intervention based on motivational interviewing and cognitive behavior therapy can help to reduce cannabis use in adolescence (Winters et al., 2021).
Review Questions
1. What was cannabis used for in the 1600s?
a. Clothes, ropes, sails, paper, and oil
b. As part of decorative wreaths
c. A natural dye
d. It was not used for anything
2. True or false: the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex are affected by marijuana.
a. True
b. False
3. What are some of the effects of marijuana?
a. Impair learning capabilities
b. Decrease motivation
c. Increased risk of mental health disorders (i.e., anxiety)
d. All of the above
References
Alcohol and Drug Foundation. (2022, June 28). Medicinal cannabis. https://adf.org.au/drug-facts/medicinal-cannabis/
Ali, S., Sardashti, M., & Sidhu, S. (2019, June 21). Marijuana Use in Teens. UNM Health Science Newsroom. https://hsc.unm.edu/news/news/marijuana-use-in-teens.html
Blest-Hopley, G., Colizzi, M., Giampietro, V., & Bhattacharyya, S. (2020). Is the adolescent brain at greater vulnerability to the effects of cannabis? A narrative review of the evidence. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00859
Bradford, A. (2017, May 18). What is THC? Live Science. https://www.livescience.com/24553-what-is-thc.html
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021, June 8). Data and statistics. https://www.cdc.gov/marijuana/data-statistics.htm#:~:text=Marijuana%20is%20the%20most%20commonly,at%20least%20once%20in%202019.&text=Recent%20research%20estimated%20that%20approximately,marijuana%20have%20marijuana%20use%20disorder.
Cyrus, E., Coudray, M.S., Kiplagat, S., Mariano, Y., Noel, I., Galea, J.T., Hadley, D., Dévieux, J.G., & Wagner, E. (2021). A review investigating the relationship between cannabis use and adolescent cognitive functioning. Current Opinion in Psychology, 38, 38-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2020.07.006
De Felice, M., Chen, C., Rodriguez-Ruiz, M., Szkudlarek, H.J., Lam, M., Sert, S., Whitehead, S.N., Yeung, K.K., Rushlow, W.J., & Laviolette, S.R. (2023). Adolescent Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol exposure induces differential acute and long-term neuronal and molecular disturbances in dorsal vs. ventral hippocampal subregions. Neuropsychopharmacology, 48(3), 540-551. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-022-01496-x
Dhein, S. (2020). Different effects of cannabis abuse on adolescent and adult brain. Pharmacology, 105, 607-615. https://doi.org/10.1159/000509377
Dutta, S.S. (2019, August 20). Hippocampus functions. News Medical & Life Sciences. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Hippocampus-Functions.aspx
Eckart, K. (2019, October 28). Teen marijuana use may have next-generation effects. University of Washington. https://www.washington.edu/news/2019/10/28/teen-marijuana-use-may-have-next-generation-effects/
Genetic Science Learning Center. (n.d.). Mouse Party. University of Utah. https://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/addiction/mouse/
Geoffrion, L. (n.d.). The effects of marijuana on the teenage and young adult brain. American Addiction Centers. https://americanaddictioncenters.org/marijuana-rehab/effects-of-marijuana-on-teenage-brain
Hammond, C. J., Chaney, A., Hendrickson, B., & Sharma, P. (2020). Cannabis use among U.S. adolescents in the era of marijuana legalization: a review of changing use patterns, comorbidity, and health correlates. International Review of Psychiatry (Abingdon, England), 32(3), 221–234. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540261.2020.1713056
History.com. (2017, May 31). Marijuana. https://www.history.com/topics/crime/history-of-marijuana
Isles, C. (2021, September 22). 7 Potential Health Benefits of Cannabis. Johnson & Wales University. https://www.jwu.edu/news/2021/09/7-potential-health-benefits-of-cannabis.html
Jacobus, J., Bava, S., Cohen-Zion, M., Mahmood, O., & Tapert, S. F. (2010). Functional consequences of marijuana use in adolescents. Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior, 92(4), 559–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2009.04.001
Leafly. (n.d.). Recreational. https://www.leafly.com/learn/cannabis-glossary/recreational
Leopold, C. (n.d.). Everything you need to know about the cerebellum. Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/313265
Mennis, J., McKeon, T.P., & Stahler, G.J. (2023). Recreational cannabis legalization alters associations among cannabis use, perception of risk, and cannabis use disorder treatment for adolescents and young adults. Addictive Behaviors, 138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2022.107552
M.J. Biz Daily. (n.d.) Where marijuana is legal in the United States. https://mjbizdaily.com/map-of-us-marijuana-legalization-by-state/
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. (2019) Cannabis (Marijuana) and Cannabinoids: What You Need to Know. NIH. Retrieved February 20, 2023, from https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/cannabis-marijuana-and-cannabinoids-what-you-need-to-know
National Institute on Drug Abuse. (2021, April 13). What are marijuana’s long-term effects on the brain?. http://nida.nih.gov/publications/research-reports/marijuana/what-are-marijuanas-long-term-effects-brain
National Institute on Drug Abuse. (2020a, January). Vaping devices (electronic cigarettes) DrugFacts. https://nida.nih.gov/publications/drugfacts/vaping-devices-electronic-cigarettes
National Institute on Drug Abuse (2020b, July) What is the scope of cannabis (marijuana) use in the United States?. NIH. https://nida.nih.gov/publications/research-reports/marijuana/what-scope-marijuana-use-in-united-states
National Institute on Drug Abuse (2019, December). Cannabis (marijuana) Drug Facts. NIH. https://nida.nih.gov/publications/drugfacts/cannabis-marijuana
Neuroscientifically Challenged. (n.d.). Know your brain: Insula. https://neuroscientificallychallenged.com/posts/what-is-insula
NORML. (n.d.) Decriminalization. https://norml.org/laws/decriminalization/
Salzman. C.D. (n.d.). Amygdala. Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/amygdala
Schmidt, S. (2021, September 20). Cannabis may alter a teen’s developing brain. Science News Explores. https://www.snexplores.org/article/cannabis-may-alter-a-teens-developing-brain
Science of Psychotherapy. (2017, January 4). Prefrontal Cortex. https://www.thescienceofpsychotherapy.com/prefrontal-cortex/#:~:text=The%20prefrontal%20cortex%20(PFC)%20is,making%2C%20and%20moderating%20social%20behaviour.
Siff, S. (2014, May). The Illegalization of Marijuana: A Brief History. Ohio State University. https://origins.osu.edu/article/illegalization-marijuana-brief-history?language_content_entity=en
Testai, F.D., Gorelick, P.B., Aparicio, H.J., Filbey, F.M, Gonzalez, R., Gottesman, R.F, Melis, M., Piano, M.R., Rubino, T., & Song, S.Y. (2022). Use of marijuana: Effect on brain health: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Stroke, 53(4), 176-187. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000396
University of Georgia. (n.d.) Survey of marijuana law in the United States: History of marijuana regulation in the United States. https://libguides.law.uga.edu/c.php?g=522835&p=3575350#:~:text=In%20the%20late%2019th%20Century,the%20recreational%20use%20of%20marijuana.
University of Wisconsin-Madison. (2019, October 22). Study: Higher social media engagement with marijuana marketing linked to higher rates of use. https://www.med.wisc.edu/news-and-events/2019/october/megan-moreno-marijuana-marketing-and-usage/
U.S. Customs and Border Protection. (n.d.) Did you know… Marijuana was once a legal cross-border import? CBP. https://www.cbp.gov/about/history/did-you-know/marijuana#:~:text=In%20principle%2C%20the%20Marihuana%20Tax,in%20this%20country%20less%20economical.
United States Drug Enforcement Administration. (n.d.) Drug scheduling. https://www.dea.gov/drug-information/drug-scheduling#:~:text=Schedule%20I%20drugs%2C%20substances%2C%20or,)%2C%20methaqualone%2C%20and%20peyote.
Volkow, N.D., Swanson, J.M., Evins, A.E., DeLisi, L.E., Meier, M.H., Gonzalez, R., Bloomfield, M.A.P., Curran, H.V., & Baler, R. (2016). Effects of cannabis use on human behavior, including cognition, motivation, and psychosis: A review. JAMA Psychiatry, 73(3), 292-297. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.3278
Weir, K. (2015). Marijuana and the developing brain. Monitor on Psychology, 46(10), 48. https://www.apa.org/monitor/2015/11/marijuana-brain
Winters, K. C., Mader, J., Budney, A. J., Stanger, C., Knapp, A. A., & Walker, D. D. (2021). Interventions for cannabis use disorder. Current Opinion in Psychology, 38, 67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2020.11.002
Ye, L., Cao, Z., Wang, W., & Zhou, N. (2019). New insights in cannabinoid receptor structure and signaling. Current Molecular Pharmacology, 12(3), 239-248. https://doi.org/10.2174%2F1874467212666190215112036
Zou, S. & Kumar, U. (2018). Cannabinoid receptors and the endocannabinoid system: Signaling and function in the central nervous system. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(3), 833. https://doi.org/10.3390%2Fijms19030833
the dried leaves, flowers, stems, and seeds of the Cannabis sativa plant
to make something that was previously illegal permissible by law
cannabis taken orally or by nasal spray to relieve symptoms of a medical condition, such as seizures, pain, and anxiety management
cannabis used for personal enjoyment that typically has higher levels of THC
the phase of life from ages 10 to 19 where a child develops into a young adult
the chemical within marijuana responsible for producing a high
the products from the Cannabis sativa plant
chemical in cannabis associated with pain relief and reducing inflammation
the action of coming to live permanently in a foreign country
of, relating to, or involving a combination of social and economic factors
a law that placed an annual tax on marijuana importers and a fine for those who did not follow the marijuana regulations
laws that reduce or remove criminal penalties faced by those possessing marijuana
any food item containing THC
a battery-operated device used to inhale an aerosol that typically contains nicotine, flavorings, and other chemicals such as THC
the mental processes involved in learning, perception, memory, attention, decision-making, and language
a brain neurotransmitter involved in the reward pathway
a neurotransmitter that plays a role in learning and memory
a local response to cellular injury characterized by redness, swelling, heat, and pain
when an individual smokes or consumes marijuana daily
a type of cell that receives and sends messages between areas of the brain and the body
area of the brain responsible for memory
a specific region in the front of the brain that plays a role in cognitive, emotional and behavioral functioning
the continued use of marijuana, even though it is causing health and social problems in one's life
physically needing a drug to function
A brief motivational enhancement intervention designed for in-school implementation that students can voluntarily participate in
a counseling approach designed to enhance someone's motivation to change
a structured, goal-oriented type of talk therapy used to treat conditions such as addictions

