29
Learning Objectives
- Set up and solve optimization problems in several applied fields.
One common application of calculus is calculating the minimum or maximum value of a function. For example, companies often want to minimize production costs or maximize revenue. In manufacturing, it is often desirable to minimize the amount of material used to package a product with a certain volume. In this section, we show how to set up these types of minimization and maximization problems and solve them by using the tools developed in this chapter.
Solving Optimization Problems over a Closed, Bounded Interval
The basic idea of the optimization problems that follow is the same. We have a particular quantity that we are interested in maximizing or minimizing. However, we also have some auxiliary condition that needs to be satisfied. For example, in (Figure) , we are interested in maximizing the area of a rectangular garden. Certainly, if we keep making the side lengths of the garden larger, the area will continue to become larger. However, what if we have some restriction on how much fencing we can use for the perimeter? In this case, we cannot make the garden as large as we like. Let’s look at how we can maximize the area of a rectangle subject to some constraint on the perimeter.
Maximizing the Area of a Garden
A rectangular garden is to be constructed using a rock wall as one side of the garden and wire fencing for the other three sides ( (Figure) ). Given 100 ft of wire fencing, determine the dimensions that would create a garden of maximum area. What is the maximum area?

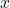 and
and 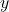 that will create a garden with a maximum area using 100 ft of fencing.
that will create a garden with a maximum area using 100 ft of fencing.Solution
Let ![]() denote the length of the side of the garden perpendicular to the rock wall and
denote the length of the side of the garden perpendicular to the rock wall and ![]() denote the length of the side parallel to the rock wall. Then the area of the garden is
denote the length of the side parallel to the rock wall. Then the area of the garden is
We want to find the maximum possible area subject to the constraint that the total fencing is ![]() From (Figure) , the total amount of fencing used will be
From (Figure) , the total amount of fencing used will be ![]() Therefore, the constraint equation is
Therefore, the constraint equation is
Solving this equation for ![]() we have
we have ![]() Thus, we can write the area as
Thus, we can write the area as
Before trying to maximize the area function ![]() we need to determine the domain under consideration. To construct a rectangular garden, we certainly need the lengths of both sides to be positive. Therefore, we need
we need to determine the domain under consideration. To construct a rectangular garden, we certainly need the lengths of both sides to be positive. Therefore, we need ![]() and
and ![]() Since
Since ![]() if
if ![]() then
then ![]() Therefore, we are trying to determine the maximum value of
Therefore, we are trying to determine the maximum value of ![]() for
for ![]() over the open interval
over the open interval ![]() We do not know that a function necessarily has a maximum value over an open interval. However, we do know that a continuous function has an absolute maximum (and absolute minimum) over a closed interval. Therefore, let’s consider the function
We do not know that a function necessarily has a maximum value over an open interval. However, we do know that a continuous function has an absolute maximum (and absolute minimum) over a closed interval. Therefore, let’s consider the function ![]() over the closed interval
over the closed interval ![]() If the maximum value occurs at an interior point, then we have found the value
If the maximum value occurs at an interior point, then we have found the value ![]() in the open interval
in the open interval ![]() that maximizes the area of the garden. Therefore, we consider the following problem:
that maximizes the area of the garden. Therefore, we consider the following problem:
Maximize ![]() over the interval
over the interval ![]()
As mentioned earlier, since ![]() is a continuous function on a closed, bounded interval, by the extreme value theorem, it has a maximum and a minimum. These extreme values occur either at endpoints or critical numbers. At the endpoints,
is a continuous function on a closed, bounded interval, by the extreme value theorem, it has a maximum and a minimum. These extreme values occur either at endpoints or critical numbers. At the endpoints, ![]() Since the area is positive for all
Since the area is positive for all ![]() in the open interval
in the open interval ![]() the maximum must occur at a critical number. Differentiating the function
the maximum must occur at a critical number. Differentiating the function ![]() we obtain
we obtain
Therefore, the only critical number is ![]() ( (Figure) ). We conclude that the maximum area must occur when
( (Figure) ). We conclude that the maximum area must occur when ![]() Then we have
Then we have ![]() To maximize the area of the garden, let
To maximize the area of the garden, let ![]() ft and
ft and ![]() The area of this garden is
The area of this garden is ![]()

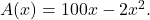
Determine the maximum area if we want to make the same rectangular garden as in (Figure) , but we have 200 ft of fencing.
Hint
We need to maximize the function ![]() over the interval
over the interval ![]()
Solution
The maximum area is ![]()
Now let’s look at a general strategy for solving optimization problems similar to (Figure) .
Problem-Solving Strategy: Solving Optimization Problems
- Introduce all variables. If applicable, draw a figure and label all variables.
- Determine which quantity is to be maximized or minimized, and for what range of values of the other variables (if this can be determined at this time).
- Write a formula for the quantity to be maximized or minimized in terms of the variables. This formula may involve more than one variable.
- Write any equations relating the independent variables in the formula from step 3. Use these equations to write the quantity to be maximized or minimized as a function of one variable.
- Identify the domain of consideration for the function in step 4 based on the physical problem to be solved.
- Locate the maximum or minimum value of the function from step 4. This step typically involves looking for critical numbers. Justify the answer using the closed interval method or another method if the interval is not closed.
- Give the final answer as a sentence with units.
Now let’s apply this strategy to maximize the volume of an open-top box given a constraint on the amount of material to be used.
Maximizing the Volume of a Box
An open-top box is to be made from a 24 in. by 36 in. piece of cardboard by removing a square from each corner of the box and folding up the flaps on each side. What size square should be cut out of each corner to get a box with the maximum volume?
Solution
Step 1: Let ![]() be the side length of the square to be removed from each corner ( (Figure) ). Then, the remaining four flaps can be folded up to form an open-top box. Let
be the side length of the square to be removed from each corner ( (Figure) ). Then, the remaining four flaps can be folded up to form an open-top box. Let ![]() be the volume of the resulting box.
be the volume of the resulting box.

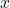 inches is removed from each corner of the piece of cardboard. The remaining flaps are folded to form an open-top box.
inches is removed from each corner of the piece of cardboard. The remaining flaps are folded to form an open-top box.Step 2: We are trying to maximize the volume of a box. Therefore, the problem is to maximize ![]()
Step 3: As mentioned in step 2, are trying to maximize the volume of a box. The volume of a box is ![]() where
where ![]() are the length, width, and height, respectively.
are the length, width, and height, respectively.
Step 4: From (Figure) , we see that the height of the box is ![]() inches, the length is
inches, the length is ![]() inches, and the width is
inches, and the width is ![]() inches. Therefore, the volume of the box is
inches. Therefore, the volume of the box is
Step 5: To determine the domain of consideration, let’s examine (Figure) . Certainly, we need ![]() Furthermore, the side length of the square cannot be greater than or equal to half the length of the shorter side, 24 in.; otherwise, one of the flaps would be completely cut off. Therefore, we are trying to determine whether there is a maximum volume of the box for
Furthermore, the side length of the square cannot be greater than or equal to half the length of the shorter side, 24 in.; otherwise, one of the flaps would be completely cut off. Therefore, we are trying to determine whether there is a maximum volume of the box for ![]() over the open interval
over the open interval ![]() Since
Since ![]() is a continuous function over the closed interval
is a continuous function over the closed interval ![]() we know
we know ![]() will have an absolute maximum over the closed interval. Therefore, we consider
will have an absolute maximum over the closed interval. Therefore, we consider ![]() over the closed interval
over the closed interval ![]() and check whether the absolute maximum occurs at an interior point.
and check whether the absolute maximum occurs at an interior point.
Step 6: Since ![]() is a continuous function over the closed, bounded interval
is a continuous function over the closed, bounded interval ![]()
![]() must have an absolute maximum (and an absolute minimum). Since
must have an absolute maximum (and an absolute minimum). Since ![]() at the endpoints and
at the endpoints and ![]() for
for ![]() the maximum must occur at a critical number. The derivative is
the maximum must occur at a critical number. The derivative is
To find the critical numbers, we need to solve the equation
Dividing both sides of this equation by 12, the problem simplifies to solving the equation
Using the quadratic formula, we find that the critical numbers are
Since ![]() is not in the domain of consideration, the only critical number we need to consider is
is not in the domain of consideration, the only critical number we need to consider is ![]() Therefore, the volume is maximized if we let
Therefore, the volume is maximized if we let ![]() The maximum volume is
The maximum volume is ![]() as shown in the following graph.
as shown in the following graph.

Watch a video about optimizing the volume of a box.
Suppose the dimensions of the cardboard in (Figure) are 20 in. by 30 in. Let ![]() be the side length of each square and write the volume of the open-top box as a function of
be the side length of each square and write the volume of the open-top box as a function of ![]() Determine the domain of consideration for
Determine the domain of consideration for ![]()
Hint
The volume of the box is ![]()
Solution
![]() The domain is
The domain is ![]()
Minimizing Travel Time
An island is ![]() due north of its closest point along a straight shoreline. A visitor is staying at a cabin on the shore that is
due north of its closest point along a straight shoreline. A visitor is staying at a cabin on the shore that is ![]() west of that point. The visitor is planning to go from the cabin to the island. Suppose the visitor runs at a rate of
west of that point. The visitor is planning to go from the cabin to the island. Suppose the visitor runs at a rate of ![]() and swims at a rate of
and swims at a rate of ![]() How far should the visitor run before swimming to minimize the time it takes to reach the island?
How far should the visitor run before swimming to minimize the time it takes to reach the island?
Solution
Step 1: Let ![]() be the distance running and let
be the distance running and let ![]() be the distance swimming ( (Figure) ). Let
be the distance swimming ( (Figure) ). Let ![]() be the time it takes to get from the cabin to the island.
be the time it takes to get from the cabin to the island.

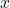 and
and 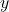 to minimize the travel time from the cabin to the island?
to minimize the travel time from the cabin to the island?Step 2: The problem is to minimize ![]()
Step 3: To find the time spent traveling from the cabin to the island, add the time spent running and the time spent swimming. Since Distance ![]() Rate
Rate ![]() Time
Time ![]() the time spent running is
the time spent running is
and the time spent swimming is
Therefore, the total time spent traveling is
Step 4: From (Figure) , the line segment of ![]() miles forms the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs of length
miles forms the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs of length ![]() and
and ![]() Therefore, by the Pythagorean theorem,
Therefore, by the Pythagorean theorem, ![]() and we obtain
and we obtain ![]() Thus, the total time spent traveling is given by the function
Thus, the total time spent traveling is given by the function
Step 5: From (Figure) , we see that ![]() Therefore,
Therefore, ![]() is the domain of consideration.
is the domain of consideration.
Step 6: Since ![]() is a continuous function over a closed, bounded interval, it has a maximum and a minimum. Let’s begin by looking for any critical numbers of
is a continuous function over a closed, bounded interval, it has a maximum and a minimum. Let’s begin by looking for any critical numbers of ![]() over the interval
over the interval ![]() The derivative is
The derivative is
If ![]() then
then
Therefore,
Squaring both sides of this equation, we see that if ![]() satisfies this equation, then
satisfies this equation, then ![]() must satisfy
must satisfy
which implies
We conclude that if ![]() is a critical number, then
is a critical number, then ![]() satisfies
satisfies
Therefore, the possibilities for critical numbers are
Since ![]() is not in the domain, it is not a possibility for a critical number. On the other hand,
is not in the domain, it is not a possibility for a critical number. On the other hand, ![]() is in the domain. Since we squared both sides of (Figure) to arrive at the possible critical numbers, it remains to verify that
is in the domain. Since we squared both sides of (Figure) to arrive at the possible critical numbers, it remains to verify that ![]() satisfies (Figure) . Since
satisfies (Figure) . Since ![]() does satisfy that equation, we conclude that
does satisfy that equation, we conclude that ![]() is a critical number, and it is the only one. To justify that the time is minimized for this value of
is a critical number, and it is the only one. To justify that the time is minimized for this value of ![]() we just need to check the values of
we just need to check the values of ![]() at the endpoints
at the endpoints ![]() and
and ![]() and compare them with the value of
and compare them with the value of ![]() at the critical number
at the critical number ![]() We find that
We find that ![]() and
and ![]() whereas
whereas ![]() Therefore, we conclude that
Therefore, we conclude that ![]() has a local minimum at
has a local minimum at ![]() mi.
mi.
Suppose the island is 1 mi from shore, and the distance from the cabin to the point on the shore closest to the island is ![]() Suppose a visitor swims at the rate of
Suppose a visitor swims at the rate of ![]() and runs at a rate of
and runs at a rate of ![]() Let
Let ![]() denote the distance the visitor will run before swimming, and find a function for the time it takes the visitor to get from the cabin to the island.
denote the distance the visitor will run before swimming, and find a function for the time it takes the visitor to get from the cabin to the island.
Hint
The time ![]()
Solution
![]()
In business, companies are interested in maximizing revenue . In the following example, we consider a scenario in which a company has collected data on how many cars it is able to lease, depending on the price it charges its customers to rent a car. Let’s use these data to determine the price the company should charge to maximize the amount of money it brings in.
Maximizing Revenue
Owners of a car rental company have determined that if they charge customers ![]() dollars per day to rent a car, where
dollars per day to rent a car, where ![]() the number of cars
the number of cars ![]() they rent per day can be modeled by the linear function
they rent per day can be modeled by the linear function ![]() If they charge
If they charge ![]() per day or less, they will rent all their cars. If they charge
per day or less, they will rent all their cars. If they charge ![]() per day or more, they will not rent any cars. Assuming the owners plan to charge customers between $50 per day and
per day or more, they will not rent any cars. Assuming the owners plan to charge customers between $50 per day and ![]() per day to rent a car, how much should they charge to maximize their revenue?
per day to rent a car, how much should they charge to maximize their revenue?
Solution
Step 1: Let ![]() be the price charged per car per day and let
be the price charged per car per day and let ![]() be the number of cars rented per day. Let
be the number of cars rented per day. Let ![]() be the revenue per day.
be the revenue per day.
Step 2: The problem is to maximize ![]()
Step 3: The revenue (per day) is equal to the number of cars rented per day times the price charged per car per day—that is, ![]()
Step 4: Since the number of cars rented per day is modelled by the linear function ![]() the revenue
the revenue ![]() can be represented by the function
can be represented by the function
Step 5: Since the owners plan to charge between ![]() per car per day and
per car per day and ![]() per car per day, the problem is to find the maximum revenue
per car per day, the problem is to find the maximum revenue ![]() for
for ![]() in the closed interval
in the closed interval ![]()
Step 6: Since ![]() is a continuous function over the closed, bounded interval
is a continuous function over the closed, bounded interval ![]() it has an absolute maximum (and an absolute minimum) in that interval. To find the maximum value, look for critical numbers. The derivative is
it has an absolute maximum (and an absolute minimum) in that interval. To find the maximum value, look for critical numbers. The derivative is ![]() Therefore, the critical number is
Therefore, the critical number is ![]() When
When ![]()
![]() When
When ![]()
![]() When
When ![]()
![]() Therefore, the absolute maximum occurs at
Therefore, the absolute maximum occurs at ![]() The car rental company should charge
The car rental company should charge ![]() per day per car to maximize revenue as shown in the following figure.
per day per car to maximize revenue as shown in the following figure.

A car rental company charges its customers ![]() dollars per day, where
dollars per day, where ![]() It has found that the number of cars rented per day can be modelled by the linear function
It has found that the number of cars rented per day can be modelled by the linear function ![]() How much should the company charge each customer to maximize revenue?
How much should the company charge each customer to maximize revenue?
Hint
![]() where
where ![]() is the number of cars rented and
is the number of cars rented and ![]() is the price charged per car.
is the price charged per car.
Solution
The company should charge ![]() per car per day.
per car per day.
Maximizing the Area of an Inscribed Rectangle
A rectangle is to be inscribed in the ellipse
What should the dimensions of the rectangle be to maximize its area? What is the maximum area?
Solution
Step 1: For a rectangle to be inscribed in the ellipse, the sides of the rectangle must be parallel to the axes. Let ![]() be the length of the rectangle and
be the length of the rectangle and ![]() be its width. Let
be its width. Let ![]() be the area of the rectangle.
be the area of the rectangle.

Step 2: The problem is to maximize ![]()
Step 3: The area of the rectangle is ![]()
Step 4: Let ![]() be the corner of the rectangle that lies in the first quadrant, as shown in (Figure) . We can write length
be the corner of the rectangle that lies in the first quadrant, as shown in (Figure) . We can write length ![]() and width
and width ![]() Since
Since ![]() and
and ![]() we have
we have ![]() Therefore, the area is
Therefore, the area is
Step 5: From (Figure) , we see that to inscribe a rectangle in the ellipse, the ![]() -coordinate of the corner in the first quadrant must satisfy
-coordinate of the corner in the first quadrant must satisfy ![]() Therefore, the problem reduces to looking for the maximum value of
Therefore, the problem reduces to looking for the maximum value of ![]() over the open interval
over the open interval ![]() Since
Since ![]() will have an absolute maximum (and absolute minimum) over the closed interval
will have an absolute maximum (and absolute minimum) over the closed interval ![]() we consider
we consider ![]() over the interval
over the interval ![]() If the absolute maximum occurs at an interior point, then we have found an absolute maximum in the open interval.
If the absolute maximum occurs at an interior point, then we have found an absolute maximum in the open interval.
Step 6: As mentioned earlier, ![]() is a continuous function over the closed, bounded interval
is a continuous function over the closed, bounded interval ![]() Therefore, it has an absolute maximum (and absolute minimum). At the endpoints
Therefore, it has an absolute maximum (and absolute minimum). At the endpoints ![]() and
and ![]()
![]() For
For ![]()
![]() Therefore, the maximum must occur at a critical number. Taking the derivative of
Therefore, the maximum must occur at a critical number. Taking the derivative of ![]() we obtain
we obtain
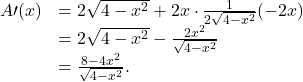
To find critical numbers, we need to find where ![]() We can see that if
We can see that if ![]() is a solution of
is a solution of
then ![]() must satisfy
must satisfy
Therefore, ![]() Thus,
Thus, ![]() are the possible solutions of (Figure) . Since we are considering
are the possible solutions of (Figure) . Since we are considering ![]() over the interval
over the interval ![]()
![]() is a possibility for a critical number, but
is a possibility for a critical number, but ![]() is not. Therefore, we check whether
is not. Therefore, we check whether ![]() is a solution of (Figure) . Since
is a solution of (Figure) . Since ![]() is a solution of (Figure) , we conclude that
is a solution of (Figure) , we conclude that ![]() is the only critical number of
is the only critical number of ![]() in the interval
in the interval ![]() Therefore,
Therefore, ![]() must have an absolute maximum at the critical number
must have an absolute maximum at the critical number ![]() To determine the dimensions of the rectangle, we need to find the length
To determine the dimensions of the rectangle, we need to find the length ![]() and the width
and the width ![]() If
If ![]() then
then
Therefore, the dimensions of the rectangle are ![]() and
and ![]() The area of this rectangle is
The area of this rectangle is ![]()
Modify the area function ![]() if the rectangle is to be inscribed in the unit circle
if the rectangle is to be inscribed in the unit circle ![]() What is the domain of consideration?
What is the domain of consideration?
Hint
If ![]() is the vertex of the square that lies in the first quadrant, then the area of the square is
is the vertex of the square that lies in the first quadrant, then the area of the square is ![]()
Solution
![]() The domain of consideration is
The domain of consideration is ![]()
Solving Optimization Problems when the Interval Is Not Closed or Is Unbounded
In the previous examples, we considered functions on closed, bounded domains. Consequently, by the extreme value theorem, we were guaranteed that the functions had absolute extrema. Let’s now consider functions for which the domain is neither closed nor bounded.
Many functions still have at least one absolute extrema, even if the domain is not closed or the domain is unbounded. For example, the function ![]() over
over ![]() has an absolute minimum of 4 at
has an absolute minimum of 4 at ![]() Therefore, we can still consider functions over unbounded domains or open intervals and determine whether they have any absolute extrema. In the next example, we try to minimize a function over an unbounded domain. We will see that, although the domain of consideration is
Therefore, we can still consider functions over unbounded domains or open intervals and determine whether they have any absolute extrema. In the next example, we try to minimize a function over an unbounded domain. We will see that, although the domain of consideration is ![]() the function has an absolute minimum. Below are the options to justify an absolute maximum or minimum of a continuous function on an open interval.
the function has an absolute minimum. Below are the options to justify an absolute maximum or minimum of a continuous function on an open interval.
Problem-Solving Strategy: Justify a Maximum or Minimum on an Open Interval
- Instead of testing the endpoints, take the limit as the variable approaches the endpoint. If both those answers are less than a critical number, then the largest function value at the critical numbers is the absolute maximum. Similar for minimum. If at least one of the limits is larger than all function values at the critical numbers (or is infinity), then there is no maximum. Similar for minimum.
- If the function is increasing over the entire interval to the left of the critical number and decreasing for the entire interval after the critical number, then there is the absolute maximum at the critical number. Similar for minimum.
- If there is only one critical number on the interval and there is a local maximum at that value, then there is an absolute maximum at that value. Similar for minimum.
In the following example, we look at constructing a box of least surface area with a prescribed volume. It is not difficult to show that for a closed-top box, by symmetry, among all boxes with a specified volume, a cube will have the smallest surface area. Consequently, we consider the modified problem of determining which open-topped box with a specified volume has the smallest surface area.
Minimizing Surface Area
A rectangular box with a square base, an open top, and a volume of 216 in. 3 is to be constructed. What should the dimensions of the box be to minimize the surface area of the box? What is the minimum surface area?
Solution
Step 1: Draw a rectangular box and introduce the variable ![]() to represent the length of each side of the square base; let
to represent the length of each side of the square base; let ![]() represent the height of the box. Let
represent the height of the box. Let ![]() denote the surface area of the open-top box.
denote the surface area of the open-top box.

Step 2: We need to minimize the surface area. Therefore, we need to minimize ![]()
Step 3: Since the box has an open top, we need only determine the area of the four vertical sides and the base. The area of each of the four vertical sides is ![]() The area of the base is
The area of the base is ![]() Therefore, the surface area of the box is
Therefore, the surface area of the box is
Step 4: Since the volume of this box is ![]() and the volume is given as
and the volume is given as ![]() the constraint equation is
the constraint equation is
Solving the constraint equation for ![]() we have
we have ![]() Therefore, we can write the surface area as a function of
Therefore, we can write the surface area as a function of ![]() only:
only:
Therefore, ![]()
Step 5: Since we are requiring that ![]() we cannot have
we cannot have ![]() Therefore, we need
Therefore, we need ![]() On the other hand,
On the other hand, ![]() is allowed to have any positive value. Note that as
is allowed to have any positive value. Note that as ![]() becomes large, the height of the box
becomes large, the height of the box ![]() becomes correspondingly small so that
becomes correspondingly small so that ![]() Similarly, as
Similarly, as ![]() becomes small, the height of the box becomes correspondingly large. We conclude that the domain is the open, unbounded interval
becomes small, the height of the box becomes correspondingly large. We conclude that the domain is the open, unbounded interval ![]() Note that, unlike the previous examples, we cannot reduce our problem to looking for an absolute maximum or absolute minimum over a closed, bounded interval. However, in the next step, we discover why this function must have an absolute minimum over the interval
Note that, unlike the previous examples, we cannot reduce our problem to looking for an absolute maximum or absolute minimum over a closed, bounded interval. However, in the next step, we discover why this function must have an absolute minimum over the interval ![]()
Step 6: Note that as ![]()
![]() Also, as
Also, as ![]()
![]() Since
Since ![]() is a continuous function that approaches infinity at the ends, it must have an absolute minimum at some
is a continuous function that approaches infinity at the ends, it must have an absolute minimum at some ![]() This minimum must occur at a critical number of
This minimum must occur at a critical number of ![]() The derivative is
The derivative is
Therefore, ![]() when
when ![]() Solving this equation for
Solving this equation for ![]() we obtain
we obtain ![]() so
so ![]() Since this is the only critical number of
Since this is the only critical number of ![]() the absolute minimum must occur at
the absolute minimum must occur at ![]() (see (Figure) ). When
(see (Figure) ). When ![]()
![]() Therefore, the dimensions of the box should be
Therefore, the dimensions of the box should be ![]() and
and ![]() With these dimensions, the surface area is
With these dimensions, the surface area is

Alternative to Step 6: As we saw before, ![]() is the only critical number of the function on our interval. Hence we can use the first or second derivative test to determine whether we have an absolute minimum. Taking the second derivative we get
is the only critical number of the function on our interval. Hence we can use the first or second derivative test to determine whether we have an absolute minimum. Taking the second derivative we get ![]() which is positive at our critical number. Therefore we get a local minimum at our critical number. Since it’s the only critical number on our interval, it’s an absolute minimum. Therefore the minimum surface area is
which is positive at our critical number. Therefore we get a local minimum at our critical number. Since it’s the only critical number on our interval, it’s an absolute minimum. Therefore the minimum surface area is ![]()
Consider the same open-top box, which is to have volume ![]() Suppose the cost of the material for the base is
Suppose the cost of the material for the base is ![]() and the cost of the material for the sides is
and the cost of the material for the sides is ![]() and we are trying to minimize the cost of this box. Write the cost as a function of the side lengths of the base. (Let
and we are trying to minimize the cost of this box. Write the cost as a function of the side lengths of the base. (Let ![]() be the side length of the base and
be the side length of the base and ![]() be the height of the box.)
be the height of the box.)
Hint
If the cost of one of the sides is ![]() the cost of that side is
the cost of that side is ![]()
Solution
![]() dollars
dollars
Key Concepts
- To solve an optimization problem, begin by drawing a picture and introducing variables.
- Find an equation relating the variables.
- Find a function of one variable to describe the quantity that is to be minimized or maximized.
- Look for critical numbers to locate local extrema.
For the following exercises, answer by proof, counterexample, or explanation.
1. When you find the maximum for an optimization problem, why do you need to check the sign of the derivative around the critical numbers?
Solution
The critical numbers can be the minima, maxima, or neither.
2. Why do you need to check the endpoints for optimization problems?
3. True or False . For every continuous nonlinear function, you can find the value ![]() that maximizes the function.
that maximizes the function.
Solution
False; ![]() has a minimum only
has a minimum only
4. True or False . For every continuous non-constant function on a closed, finite domain, there exists at least one ![]() that minimizes or maximizes the function.
that minimizes or maximizes the function.
For the following exercises, set up and evaluate each optimization problem.
5. To carry a suitcase on an airplane, the length ![]() height of the box must be less than or equal to
height of the box must be less than or equal to ![]() Assuming the height is fixed, show that the maximum volume is
Assuming the height is fixed, show that the maximum volume is ![]() What height allows you to have the largest volume?
What height allows you to have the largest volume?
Solution
![]() in.
in.
6. You are constructing a cardboard box with the dimensions ![]() You then cut equal-size squares from each corner so you may fold the edges. What are the dimensions of the box with the largest volume?
You then cut equal-size squares from each corner so you may fold the edges. What are the dimensions of the box with the largest volume?

7. Find the positive integer that minimizes the sum of the number and its reciprocal.
Solution
1
8. Find two positive integers such that their sum is 10, and minimize and maximize the sum of their squares.
For the following exercises, consider the construction of a pen to enclose an area.
9. You have ![]() of fencing to construct a rectangular pen for cattle. What are the dimensions of the pen that maximize the area?
of fencing to construct a rectangular pen for cattle. What are the dimensions of the pen that maximize the area?
Solution
![]()
10. You have ![]() of fencing to make a pen for hogs. If you have a river on one side of your property, what is the dimension of the rectangular pen that maximizes the area?
of fencing to make a pen for hogs. If you have a river on one side of your property, what is the dimension of the rectangular pen that maximizes the area?
11. You need to construct a fence around an area of ![]() What are the dimensions of the rectangular pen to minimize the amount of material needed?
What are the dimensions of the rectangular pen to minimize the amount of material needed?
Solution
![]()
12. Two poles are connected by a wire that is also connected to the ground. The first pole is ![]() tall and the second pole is
tall and the second pole is ![]() tall. There is a distance of
tall. There is a distance of ![]() between the two poles. Where should the wire be anchored to the ground to minimize the amount of wire needed?
between the two poles. Where should the wire be anchored to the ground to minimize the amount of wire needed?

13. [T] You are moving into a new apartment and notice there is a corner where the hallway narrows from ![]() What is the length of the longest item that can be carried horizontally around the corner?
What is the length of the longest item that can be carried horizontally around the corner?

Solution
![]()
14. A patient’s pulse measures ![]() To determine an accurate measurement of pulse, the doctor wants to know what value minimizes the expression
To determine an accurate measurement of pulse, the doctor wants to know what value minimizes the expression ![]() What value minimizes it?
What value minimizes it?
15. In the previous problem, assume the patient was nervous during the third measurement, so we only weight that value half as much as the others. What is the value that minimizes ![]()
Solution
![]()
16. You can run at a speed of 6 mph and swim at a speed of 3 mph and are located on the shore, 4 miles east of an island that is 1 mile north of the shoreline. How far should you run west to minimize the time needed to reach the island?

For the following problems, consider a lifeguard at a circular pool with diameter ![]() He must reach someone who is drowning on the exact opposite side of the pool, at position
He must reach someone who is drowning on the exact opposite side of the pool, at position ![]() The lifeguard swims with a speed
The lifeguard swims with a speed ![]() and runs around the pool at speed
and runs around the pool at speed ![]()

17. Find a function that measures the total amount of time it takes to reach the drowning person as a function of the swim angle, ![]()
Solution
![]()
18. Find at what angle ![]() the lifeguard should swim to reach the drowning person in the least amount of time.
the lifeguard should swim to reach the drowning person in the least amount of time.
19. A truck uses gas as ![]() where
where ![]() represents the speed of the truck and
represents the speed of the truck and ![]() represents the gallons of fuel per mile. At what speed is fuel consumption minimized?
represents the gallons of fuel per mile. At what speed is fuel consumption minimized?
Solution
![]()
For the following exercises, consider a limousine that gets ![]() at speed
at speed ![]() the chauffeur costs
the chauffeur costs ![]() and gas is
and gas is ![]()
20. Find the cost per mile at speed ![]()
21. Find the cheapest driving speed.
Solution
approximately ![]()
For the following exercises, consider a pizzeria that sell pizzas for a revenue of ![]() and costs
and costs ![]() where
where ![]() represents the number of pizzas.
represents the number of pizzas.
22. Find the profit function for the number of pizzas. How many pizzas gives the largest profit per pizza?
23. Assume that ![]() and
and ![]() How many pizzas sold maximizes the profit?
How many pizzas sold maximizes the profit?
Solution
4
24. Assume that ![]() and
and ![]() How many pizzas sold maximizes the profit?
How many pizzas sold maximizes the profit?
For the following exercises, consider a wire ![]() long cut into two pieces. One piece forms a circle with radius
long cut into two pieces. One piece forms a circle with radius ![]() and the other forms a square of side
and the other forms a square of side ![]()
25. Choose ![]() to maximize the sum of their areas.
to maximize the sum of their areas.
Solution
0
26. Choose ![]() to minimize the sum of their areas.
to minimize the sum of their areas.
For the following exercises, consider two nonnegative numbers ![]() and
and ![]() such that
such that ![]() Maximize and minimize the quantities.
Maximize and minimize the quantities.
27. ![]()
Solution
Maximal: ![]() minimal:
minimal: ![]() and
and ![]()
28. ![]()
29. ![]()
Solution
Maximal: ![]() minimal: none
minimal: none
30. ![]()
For the following exercises, draw the given optimization problem and solve.
31. Find the volume of the largest right circular cylinder that fits in a sphere of radius 1.
Solution
![]()
32. Find the volume of the largest right cone that fits in a sphere of radius 1.
33. Find the area of the largest rectangle that fits into the triangle with sides ![]() and
and ![]()
Solution
6
34. Find the largest volume of a cylinder that fits into a cone that has base radius ![]() and height
and height ![]()
35. Find the dimensions of the closed cylinder volume ![]() that has the least amount of surface area.
that has the least amount of surface area.
Solution
![]()
36. Find the dimensions of a right cone with surface area ![]() that has the largest volume.
that has the largest volume.
For the following exercises, consider the points on the given graphs. Use a calculator to graph the functions.
37. [T] Where is the line ![]() closest to the origin?
closest to the origin?
Solution
![]()
38. [T] Where is the line ![]() closest to point
closest to point ![]()
39. [T] Where is the parabola ![]() closest to point
closest to point ![]()
Solution
![]()
40. [T] Where is the parabola ![]() closest to point
closest to point ![]()
For the following exercises, set up, but do not evaluate, each optimization problem.
41. A window is composed of a semicircle placed on top of a rectangle. If you have ![]() of window-framing materials for the outer frame, what is the maximum size of the window you can create? Use
of window-framing materials for the outer frame, what is the maximum size of the window you can create? Use ![]() to represent the radius of the semicircle.
to represent the radius of the semicircle.

Solution
![]()
42. You have a garden row of 20 watermelon plants that produce an average of 30 watermelons apiece. For any additional watermelon plants planted, the output per watermelon plant drops by one watermelon. How many extra watermelon plants should you plant?
43. You are constructing a box for your cat to sleep in. The plush material for the square bottom of the box costs ![]() and the material for the sides costs
and the material for the sides costs ![]() You need a box with volume
You need a box with volume ![]() Find the dimensions of the box that minimize cost. Use
Find the dimensions of the box that minimize cost. Use ![]() to represent the length of the side of the box.
to represent the length of the side of the box.
Solution
![]()
44. You are building five identical pens adjacent to each other with a total area of ![]() as shown in the following figure. What dimensions should you use to minimize the amount of fencing?
as shown in the following figure. What dimensions should you use to minimize the amount of fencing?

45. You are the manager of an apartment complex with 50 units. When you set rent at ![]() all apartments are rented. As you increase rent by
all apartments are rented. As you increase rent by ![]() one fewer apartment is rented. Maintenance costs run
one fewer apartment is rented. Maintenance costs run ![]() for each occupied unit. What is the rent that maximizes the total amount of profit?
for each occupied unit. What is the rent that maximizes the total amount of profit?
Solution
![]()
Glossary
- optimization problems
- problems that are solved by finding the maximum or minimum value of a function

