11
True or False. In the following exercises, justify your answer with a proof or a counterexample.
1. A function has to be continuous at ![]() if the
if the ![]() exists.
exists.
2. You can use the quotient rule to evaluate ![]() .
.
Solution
False
3. If there is a vertical asymptote at ![]() for the function
for the function ![]() , then
, then ![]() is undefined at the point
is undefined at the point ![]() .
.
4. If ![]() does not exist, then
does not exist, then ![]() is undefined at the point
is undefined at the point ![]() .
.
Solution
False. A removable discontinuity is possible.
5. Using the graph of ![]() , find each of the following or explain why it does not exist.
, find each of the following or explain why it does not exist.

In the following exercises, evaluate the limit algebraically or explain why the limit does not exist.
6. ![]()
Solution
5
7. ![]()
8. ![]()
Solution
![]()
9. ![]()
10. ![]()
Solution
DNE
11. ![]()
12. ![]()
Solution
![]()
13. ![]()
14. ![]()
Solution
−4
15. ![]()
16. ![]()
Solution
![]()
17. ![]()
18. ![]()
Solution
2
19. ![]()
20. ![]()
Solution
![]()
21. ![]()
22. ![]()
Solution
![]()
23. ![]()
24. ![]()
Solution
![]()
25. ![]()
In the following exercises, evaluate the limits to infinity.
26. ![]()
Solution
![]()
27. ![]()
28. ![]()
Solution
![]()
29. ![]()
30. ![]()
Solution
![]()
31. ![]()
In the following exercises, use the squeeze theorem to prove the limit.
32. ![]()
Solution
Since ![]() , then
, then ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() , it follows that
, it follows that ![]() .
.
33. ![]()
34. ![]()
Solution
Since ![]() , then
, then ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() , it follows that
, it follows that ![]() .
.
In the following exercises, determine the value of ![]() such that the function is continuous for the given value of
such that the function is continuous for the given value of ![]() .
.
35. 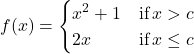
36. 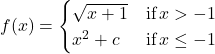
Solution
![]()
37. 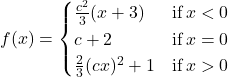
38. 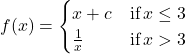
Solution
![]()
In the following exercises, determine all horizontal and vertical asymptotes.
39. ![]()
40. ![]()
Solution
Horizontal: ![]() , Vertical:
, Vertical: ![]()
41. ![]()
42. ![]()
Solution
Horizontal: ![]() , Vertical: none
, Vertical: none
In the following exercises, use the Intermediate Value Theorem to show that the given functions have an x-intercept in the given interval.
43. ![]() on the interval
on the interval ![]()
44. ![]() on the interval
on the interval ![]()
Solution
Since ![]() is continuous on [-2,-1] and
is continuous on [-2,-1] and ![]() and
and ![]() , then by IVT, there exists a root on the given interval.
, then by IVT, there exists a root on the given interval.
45. A ball is thrown into the air and the vertical position is given by ![]() . Use the Intermediate Value Theorem to show that the ball must land on the ground sometime between 5 sec and 6 sec after the throw.
. Use the Intermediate Value Theorem to show that the ball must land on the ground sometime between 5 sec and 6 sec after the throw.
46. A particle moving along a line has a displacement according to the function ![]() , where
, where ![]() is measured in meters and
is measured in meters and ![]() is measured in seconds. Find the average velocity over the time period
is measured in seconds. Find the average velocity over the time period ![]() .
.
Solution
![]() m/sec
m/sec
In the following exercises, use the precise definition of limit to prove the limit.
47. ![]()
48. ![]()
Solution
![]()

