17
Learning Objectives
- Find the derivatives of the sine and cosine function.
- Find the derivatives of the standard trigonometric functions.
- Calculate the higher-order derivatives of the sine and cosine.
One of the most important types of motion in physics is simple harmonic motion, which is associated with such systems as an object with mass oscillating on a spring. Simple harmonic motion can be described by using either sine or cosine functions. In this section we expand our knowledge of derivative formulas to include derivatives of these and other trigonometric functions. We begin with the derivatives of the sine and cosine functions and then use them to obtain formulas for the derivatives of the remaining four trigonometric functions. Being able to calculate the derivatives of the sine and cosine functions will enable us to find the velocity and acceleration of simple harmonic motion.
Derivatives of the Sine and Cosine Functions
We begin our exploration of the derivative for the sine function by using the formula to make a reasonable guess at its derivative. Recall that for a function ![]()
Consequently, for values of ![]() very close to 0,
very close to 0, ![]() . We see that by using
. We see that by using ![]() ,
,
By setting ![]() and using a graphing utility, we can get a graph of an approximation to the derivative of
and using a graphing utility, we can get a graph of an approximation to the derivative of ![]() ( (Figure) ).
( (Figure) ).

 looks a lot like a cosine curve.
looks a lot like a cosine curve.Upon inspection, the graph of ![]() appears to be very close to the graph of the cosine function. Indeed, we will show that
appears to be very close to the graph of the cosine function. Indeed, we will show that
If we were to follow the same steps to approximate the derivative of the cosine function, we would find that
The Derivatives of  and
and 
The derivative of the sine function is the cosine and the derivative of the cosine function is the negative sine.
Proof
Because the proofs for ![]() and
and ![]() use similar techniques, we provide only the proof for
use similar techniques, we provide only the proof for ![]() . Before beginning, recall two important trigonometric limits we learned in Introduction to Limits :
. Before beginning, recall two important trigonometric limits we learned in Introduction to Limits :
The graphs of ![]() and
and ![]() are shown in (Figure) .
are shown in (Figure) .

We also recall the following trigonometric identity for the sine of the sum of two angles:
Now that we have gathered all the necessary equations and identities, we proceed with the proof.

(Figure) shows the relationship between the graph of ![]() and its derivative
and its derivative ![]() . Notice that at the points where
. Notice that at the points where ![]() has a horizontal tangent, its derivative
has a horizontal tangent, its derivative ![]() takes on the value zero. We also see that where
takes on the value zero. We also see that where ![]() is increasing,
is increasing, ![]() and where
and where ![]() is decreasing,
is decreasing, ![]() .
.

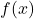 has a maximum or a minimum,
has a maximum or a minimum,  . That is,
. That is,  where
where 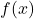 has a horizontal tangent. These points are noted with dots on the graphs.
has a horizontal tangent. These points are noted with dots on the graphs.Differentiating a Function Containing 
Find the derivative of ![]() .
.
Solution
Using the product rule, we have
After simplifying, we obtain
Find the derivative of ![]()
Hint
Don’t forget to use the product rule.
Solution
![]()
Finding the Derivative of a Function Containing 
Find the derivative of ![]() .
.
Solution
By applying the quotient rule, we have
Simplifying, we obtain
Find the derivative of ![]() .
.
Hint
Use the quotient rule.
Solution
![]()
An Application to Velocity
A particle moves along a coordinate axis in such a way that its position at time ![]() is given by
is given by ![]() for
for ![]() . At what times is the particle at rest?
. At what times is the particle at rest?
Solution
To determine when the particle is at rest, set ![]() . Begin by finding
. Begin by finding ![]() . We obtain
. We obtain
so we must solve
The solutions to this equation are ![]() and
and ![]() . Thus the particle is at rest at times
. Thus the particle is at rest at times ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
A particle moves along a coordinate axis. Its position at time ![]() is given by
is given by ![]() for
for ![]() . At what times is the particle at rest?
. At what times is the particle at rest?
Hint
Use the previous example as a guide.
Solution
![]()
Derivatives of Other Trigonometric Functions
Since the remaining four trigonometric functions may be expressed as quotients involving sine, cosine, or both, we can use the quotient rule to find formulas for their derivatives.
The Derivative of the Tangent Function
Find the derivative of ![]() .
.
Solution
Start by expressing ![]() as the quotient of
as the quotient of ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
Now apply the quotient rule to obtain
Simplifying, we obtain
Recognizing that ![]() , by the Pythagorean Identity, we now have
, by the Pythagorean Identity, we now have
Finally, use the identity ![]() to obtain
to obtain
Find the derivative of ![]() .
.
Hint
Rewrite ![]() as
as ![]() and use the quotient rule.
and use the quotient rule.
Solution
![]()
The derivatives of the remaining trigonometric functions may be obtained by using similar techniques. We provide these formulas in the following theorem.
Derivatives of  , and
, and 
The derivatives of the remaining trigonometric functions are as follows:
Finding the Equation of a Tangent Line
Find the equation of a line tangent to the graph of ![]() at
at ![]() .
.
Solution
To find the equation of the tangent line, we need a point and a slope at that point. To find the point, compute
Thus the tangent line passes through the point ![]() . Next, find the slope by finding the derivative of
. Next, find the slope by finding the derivative of ![]() and evaluating it at
and evaluating it at ![]() :
:
Using the point-slope equation of the line, we obtain
or equivalently,
Finding the Derivative of Trigonometric Functions
Find the derivative of ![]()
Solution
To find this derivative, we must use both the sum rule and the product rule. Using the sum rule, we find
In the first term, ![]() , and by applying the product rule to the second term we obtain
, and by applying the product rule to the second term we obtain
Therefore, we have
Find the derivative of ![]() .
.
Hint
Use the rule for differentiating a constant multiple and the rule for differentiating a difference of two functions.
Solution
![]()
Find the slope of the line tangent to the graph of ![]() at
at ![]() .
.
Hint
Evaluate the derivative at ![]() .
.
Solution
![]()
Higher-Order Derivatives
The higher-order derivatives of ![]() and
and ![]() follow a repeating pattern. By following the pattern, we can find any higher-order derivative of
follow a repeating pattern. By following the pattern, we can find any higher-order derivative of ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Finding Higher-Order Derivatives of 
Find the first four derivatives of ![]() .
.
Solution
Each step in the chain is straightforward:

Analysis
Once we recognize the pattern of derivatives, we can find any higher-order derivative by determining the step in the pattern to which it corresponds. For example, every fourth derivative of ![]() equals
equals ![]() , so
, so

For ![]() , find
, find ![]() .
.
Hint
See the previous example.
Solution
![]()
Using the Pattern for Higher-Order Derivatives of 
Find ![]() .
.
Solution
We can see right away that for the 74th derivative of ![]() , so
, so
For ![]() , find
, find ![]() .
.
Hint
![]()
Solution
![]()
An Application to Acceleration
A particle moves along a coordinate axis in such a way that its position at time ![]() is given by
is given by ![]() . Find
. Find ![]() and
and ![]() . Compare these values and decide whether the particle is speeding up or slowing down.
. Compare these values and decide whether the particle is speeding up or slowing down.
First find ![]() :
: ![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() . Next, find
. Next, find ![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() and we have
and we have ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() and
and ![]() , we see that velocity and acceleration are acting in opposite directions; that is, the object is being accelerated in the direction opposite to the direction in which it is travelling. Consequently, the particle is slowing down.
, we see that velocity and acceleration are acting in opposite directions; that is, the object is being accelerated in the direction opposite to the direction in which it is travelling. Consequently, the particle is slowing down.
A block attached to a spring is moving vertically. Its position at time ![]() is given by
is given by ![]() . Find
. Find ![]() and
and ![]() . Compare these values and decide whether the block is speeding up or slowing down.
. Compare these values and decide whether the block is speeding up or slowing down.
Hint
Use (Figure) as a guide.
Solution
![]() and
and ![]() . The block is speeding up.
. The block is speeding up.
Key Concepts
- We can find the derivatives of
 and
and  by using the definition of derivative and the limit formulas found earlier. The results are
by using the definition of derivative and the limit formulas found earlier. The results are
 and
and  .
. - With these two formulas, we can determine the derivatives of all six basic trigonometric functions.
Key Equations
- Derivative of sine function

- Derivative of cosine function

- Derivative of tangent function

- Derivative of cotangent function

- Derivative of secant function

- Derivative of cosecant function

For the following exercises, find ![]() for the given functions.
for the given functions.
1. ![]()
Solution
![]()
2. ![]()
3. ![]()
Solution
![]()
4. ![]()
5. ![]()
Solution
![]()
6. ![]()
7. ![]()
Solution
![]()
8. ![]()
9. ![]()
Solution
![]()
10. ![]()
For the following exercises, find the equation of the tangent line to each of the given functions at the indicated values of ![]() . Then use a calculator to graph both the function and the tangent line to ensure the equation for the tangent line is correct.
. Then use a calculator to graph both the function and the tangent line to ensure the equation for the tangent line is correct.
11. [T] ![]()
Solution
![]()

12. [T] ![]()
13. [T] ![]()
Solution
![]()

14. [T] ![]()
15. [T] ![]()
![]()

16. [T] ![]()
For the following exercises, find ![]() for the given functions.
for the given functions.
17. ![]()
Solution
![]()
18. ![]()
19. ![]()
Solution
![]()
20. ![]()
21. ![]()
Solution
![]()
22. ![]()
23. Find all ![]() values on the graph of
values on the graph of ![]() where the tangent line is horizontal.
where the tangent line is horizontal.
Solution
![]() , where
, where ![]() is an integer
is an integer
24. Find all ![]() values on the graph of
values on the graph of ![]() for
for ![]() where the tangent line has a slope of 2.
where the tangent line has a slope of 2.
25. Let ![]() . Determine the point(s) on the graph of
. Determine the point(s) on the graph of ![]() for
for ![]() where the tangent line is parallel to the line
where the tangent line is parallel to the line ![]() .
.
Solution
![]()
26. [T] A mass on a spring bounces up and down in simple harmonic motion, modeled by the function ![]() where
where ![]() is measured in inches and
is measured in inches and ![]() is measured in seconds. Find the rate at which the spring is oscillating at
is measured in seconds. Find the rate at which the spring is oscillating at ![]() s.
s.
27. Let the position of a swinging pendulum in simple harmonic motion be given by ![]() . Find the constants
. Find the constants ![]() and
and ![]() such that when the velocity is 3 cm/s,
such that when the velocity is 3 cm/s, ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Solution
![]()
28. After a diver jumps off a diving board, the edge of the board oscillates with position given by ![]() cm at
cm at ![]() seconds after the jump.
seconds after the jump.
- Sketch one period of the position function for
 .
. - Find the velocity function.
- Sketch one period of the velocity function for
 .
. - Determine the times when the velocity is 0 over one period.
- Find the acceleration function.
- Sketch one period of the acceleration function for
 .
.
29. The number of hamburgers sold at a fast-food restaurant in Pasadena, California, is given by ![]() where
where ![]() is the number of hamburgers sold and
is the number of hamburgers sold and ![]() represents the number of hours after the restaurant opened at 11 a.m. until 11 p.m., when the store closes. Find
represents the number of hours after the restaurant opened at 11 a.m. until 11 p.m., when the store closes. Find ![]() and determine the intervals where the number of burgers being sold is increasing.
and determine the intervals where the number of burgers being sold is increasing.
Solution
![]() , increasing on
, increasing on ![]() , and
, and ![]()
30. [T] The amount of rainfall per month in Phoenix, Arizona, can be approximated by ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the number of months since January. Find
is the number of months since January. Find ![]() and use a calculator to determine the intervals where the amount of rain falling is decreasing.
and use a calculator to determine the intervals where the amount of rain falling is decreasing.
For the following exercises, use the quotient rule to derive the given equations.
31. ![]()
32. ![]()
33. ![]()
34. Use the definition of derivative and the identity
![]() to prove that
to prove that ![]() .
.
For the following exercises, find the requested higher-order derivative for the given functions.
35. ![]() of
of ![]()
36. ![]() of
of ![]()
37. ![]() of
of ![]()
Solution
![]()
38. ![]() of
of ![]()
39. ![]() of
of ![]()
Solution
![]()
40. ![]() of
of ![]() . Notation:
. Notation: ![]() is the 24th derivative of
is the 24th derivative of ![]() .
.
41. ![]() of
of ![]()
Solution
![]()
For the following exercises, determine the limits. Use the fact that ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
42. ![]()
43. ![]()
Solution
![]()
44. ![]()
45. ![]()
Solution
![]()
46. ![]()
47. ![]()
Solution
![]()

