33 Mental Health in Social Media
Mia Manfredi
33.1 Introduction
Keywords
- Anorexia– a mental disorder marked by an obsession with losing weight by refusing to eat
- Agoraphobia– extreme or illogical dread of entering crowded or open spaces, of leaving one’s home, or of being in situations where escape is difficult
- ED– eating disorder
Learning Objectives
- By the end of this chapter, students will be able to:
Learn how social media has heavily affected individuals of all ages - Recognize how social media can cause a variety of mental disorders.
- Identify all the different types of mental disorders
Programs that run on mobile phones and desktop platforms and rely on the internet’s ability to produce and distribute information are referred to as social media. The seeming growth of promising technology has altered how civil society connects and communicates in their daily activities. People use social media to stay in touch with loved ones all over the world, as a source of entertainment, and as a key to information. While social media has a major impact on the world, excessive use can lead to feelings of anxiety, depression, fear of missing out, and loneliness. Social media, particularly in the fitness industry, is a strong tool. Fitness narratives on social platforms involve influencers claiming to be mentors in hopes of motivating others to live a better lifestyle. They achieve this by publishing photographs and films of what they regard as a desirable physique of a man or woman on their platforms. Influencers are pushing for healthy diet eating to achieve a certain body shape. All the focus is on selfies, huge muscles, toned bodies, and before and after photos. This type of content triggers vulnerable people with fear missing out on the trend of the obsessive exercise with image and fitness with eating disorders such as Anorexia as they try to restrict themselves from eating certain foods or even starve to get into shape. Social media is the most popular version of communication used in the 21st century. Individuals of all ages use social media as a gateway and a form of education. With so many hours spent on social media platforms, mental health has become an issue. Social media has affected mental health negatively based on unrealistic promotions, eating disorders. and body imaging issues.

“Mental Health Word Cloud” by Pixabay is licensed under CC0 1.0
33.2 What is mental health?
Key Takeaway
Our emotional, psychological, and social well-being are all part of our mental health. It has an impact on the way we think, feel, and act. It also influences how we deal with stress, interact with others, and make decisions. Mental health is vital at all stages of life, including childhood, adolescence, and maturity. Mental illness can also have an impact on daily life, relationships, and physical health. Everyone, regardless of age, sex, income, or race, is at risk of acquiring a mental health issue. A person’s mental health can be influenced by social and socioeconomic situations, biological variables, and lifestyle choices.
There are many different disorders that can develop from mental health. There are anxiety disorders (which are the most common), panic disorders, phobias, obsessive-compulsive disorders, post-trauma disorders, mood disorders, and eating disorders. Anxiety and panic disorders develop from social situations. Individuals with anxiety disorders may have extreme anxiety when confronted with daily tasks that do not pose a direct threat, such as doing chores or making appointments. A person with GAD (General Anxiety Disorder) may experience anxiety without any apparent cause. A person with a panic disorder can experience panic attacks, which include abrupt, overpowering anxiety or a sense of impending calamity and death, which are common in people with panic disorders.
Phobias can also be developed. There are simple phobias, social phobias, and agoraphobias. Simple phobias could be an exaggerated dread of certain objects, scenarios, or animals. For example, a fear of snakes or spiders. Social phobias can result from social anxiety and the fear of being “judged by someone”. Agoraphobia is the dread of being trapped in a scenario where getting out is difficult, such as an elevator or a moving train. Many individuals mistake this phobia for a fear of the outdoors.
33.3 How mental disorders develops
Key Takeaway
Mental disorders can develop by genetics, psychological, or environmental factors. Mental diseases are known to run in families, so people who have a family member who suffers from one may be more prone to develop one themselves. It is handed down through the generations via genes. Many mental diseases, according to experts, are linked to defects in multiple genes rather than just one or two, and that the way these genes interact with the environment is different for each person (even identical twins). That is why someone can inherit a vulnerability to mental disease but not necessarily develop it. The combination of several genes and other circumstances causes mental disease. Infections and brain defects also can cause mental disorders to develop. Certain infections have been related to brain damage, as well as the onset or aggravation of mental disorder. Environmental factors contribute to mental illness as well by certain stressors and triggers. An example of this is a death or divorce, any change in an individual’s environment. Also low self esteem, rage, or loneliness or the relocation of a school or job.
33.4 Effects of social media on mental health
Key Takeaway
How social media has affected individuals’ mental health. How social media causes mental and eating disorders due to body shaming and imaging.
Individuals of all ages are glued to their phone, more specifically social media. Everyone wants to know what each other are doing and what is going on in each other’s lives. People also go to social media for inspiration, recipes, or ideas. People usually look for “influencers” to gain knowledge about everything. They look for a larger following and the most popular because it is the social norm to want to follow the group and to be “trendy” and follow what everyone else is doing.
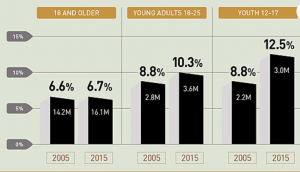
“NSDUH_0004_MentalHealth” by SAMASHA is in the public domain
No one can disagree that these influencers and other social media stars have the best of intentions when it comes to sharing their tips. Whether it is health tips or decorating, or advice, etc. Despite advocating self-acceptance and self-love, there is still a considerable disconnect between the photos uploaded and the motivational statements that accompany them on social media. For example many influencers are known for their following for health tips or because of their physic. Due to continual exposure to photos that are so precisely posed, promoting programs that promise the same body in 6 weeks, participants are participating in actions that are well beyond the grasp of a healthy lifestyle. In their pursuit of the “ideal” body type, users are damaging themselves, or rather, the photo they’re shown sets the bar higher than it should be (Berryman et al.). To achieve the perfect Instagram figure, it leads to a terrible connection with food, excessive exercise, or injuries, leaving you bewildered as to why your results aren’t the same, which harms an individual’s self-esteem. According to mental health experts, social media profiles do not promote good diet and physical activity. Influencers with eating disorders and body image concerns have been discovered, and they are inadvertently pushing their behaviors and troubles onto people who are vulnerable. The need to keep a trim, toned body becomes a source of affirmation and acceptance. Unfortunately, research shows that this obsession with achieving a certain body type has negative effects on body image. It also increases the risk of developing eating disorders, compulsive exercise, and disordered eating.
33.5 Future of mental health in social media
Key Takeaway
Mental health/ disorders have been a common effect due to social media. In order to help individuals, many groups have been put together to try and stop the mental abuse. There is a “body positivity” movement over all social media platforms where influencers and stars post their most realistic and photoshopped images of themselves to show that everyone has flaws and to not be ashamed of them. The body positivity movement has helped millions of people to overcome their disorders and influence them to help others.
There is also an “ed recovery” movement over all platforms. This movement helps those with eating disorders recover from their starvation and shows them new recipes and a healthier way of living to sustain themselves without harm.
Case Study
Case Study: Merideth Foster’s Recovery
A well known social media influencer “Meredith Foster” over the span of a year lost an excessive amount of weight. She continues to lose weight even when she said she reached her goal. Her friends became concerned, and would ask her about it but she went on as nothing was happening and neglected her friends because of the harassment about her weight. Two years went by and Meredith came out with a youtube video explaining her story. The content was how social media put out “a specific version” of how someone should look. Meredith would constantly pick apart images of herself and read the hatred comments, which would just consume her mentally. While reading the comments, she believed them and thought she had to do everything she could to “get rid of arm fat” or “get rid of back fat”. The hatred led to her starving herself, and to only eat an apple a day, or carrots a day, some days not even eating at all. She finally realized that this was not a way to live and chose recovery. She started therapy and met with a nutritionist and now lives a happy and healthy lifestyle.
Chapter Summary
Overall this chapter goes through what mental health is and all the variety of mental disorders that can develop in an individual. Also how social media is one of the main causes for these mental disorders, and how influencers and the social media content can affect people of all ages.
Review Questions
1. What causes a mental order to develop?
A. Biological factors
B. Psychological
C. Environmental factors
D. All of the above
2. What are the best options for helping a mental disorder?
A. therapy/group help
B. Doing nothing
C. Go to Mcdonalds
D. Go to sleep
3. What type of mental disorder is the most common?
A. Agoraphobia
B. Social disorders
C. Anxiety disorders
4. Can mental disorders be developed through trauma?
A. Yes
B. No
C. I don’t know
Answers
- D
- A
- C
- A
Food for Thought
- Do you think mental health and disorders became more known after the over use of social media platforms?
- What do you think the newest generation would be like if social media was not developed?
References
Corrigan, P. W., Watson, A. C., Byrne, P., & Davis, K. E. (2005). Mental illness stigma: Problem of public health or social justice? Social Work, 50(4), 363–368. http://www.jstor.org/stable/23721317.
Fleps, A. B. B. (2021, April 21). Social media effects on body image and eating disorders. News. Retrieved November 9, 2021, from https://news.illinoisstate.edu/2021/04/social-media-effects-on-body-image-and-eating-disorders/.
Link between social media & body image. King University Online. (n.d.). Retrieved November 9, 2021, from https://online.king.edu/news/social-media-and-body-image/.
Impact of social media on Youth Mental Health. University ofNevada, Reno. (2019, December 30). Retrieved November 9, 2021, from https://onlinedegrees.unr.edu/online-master-of-public-health/impact-of-social-media-on-youth-mental-health/.
Meredith Elaine Foster. YouTube. Retrieved November 18, 2021, from http://bit.ly/SubscribeMeredithFoster.
Robinson, L. (2021, October 7). Social Media and Mental Health. HelpGuide.org. Retrieved November 2, 2021, from https://www.helpguide.org/articles/mental-health/social-media-and-mental-health.htm.
Subrahmanyam, K., & Greenfield, P. (2008). Online communication and adolescent relationships. The Future of Children, 18(1), 119–146. http://www.jstor.org/stable/20053122.
The social dilemma: Social media and your mental health. Here’s How Social Media Affects Your Mental Health | McLean Hospital. (2021, February 9). Retrieved November 2, 2021, from https://www.mcleanhospital.org/essential/it-or-not-social-medias-affecting-your-mental-health.
A mental disorder marked by an obsession with losing weight by refusing to eat.
A mental disorder marked by an obsession with losing weight by refusing to eat.

